What is Lean six sigma?
- Lean six sigma is a collaborative effort of improving the entire process by using various statistical tools and reducing and eventually eliminating the waste from the process to ensure maximum efficiency.
Six sigma:
Six Sigma focuses on high-level cross-functional processes, with involvement from upper management and it relies on experts to implement various tools. Six sigma generally uses simple tools for process improvement, but these simple tools can be very powerful. It is important to use the approach that fits the situation. Six Sigma uses a five-step model called DMAIC, to shape improvement projects and focuses on outcomes in terms of benefits for the company. Six Sigma focuses on reducing variation, measuring defects, and improving the quality of products, processes, and services.
Lean:
Lean is about creating value and eliminating waste to reduce costs and improve efficiency, productivity, and quality. Lean is a way of looking at how we do things and removing as much waste as possible so the end customer gets the most value. In this process, the resources that are not adding value in one place are removed and then reused in some other area where they will add value. While the goal is to reduce waste and create the most value for the customer, Lean also makes things better for employees and the organization.
Difference between lean and six sigma:
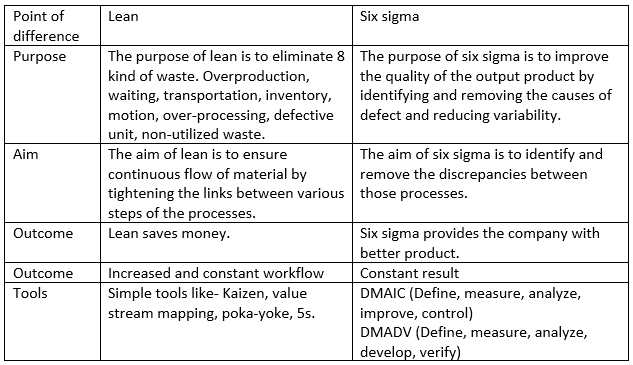
Difference between lean six sigma and six sigma:
Lean six sigma process:
As we discussed earlier, lean is a process that focuses on:
- Providing value to the customer
- Eliminating waste
- Continuous improvement
- Reducing cycle time
The main target of lean is to handle the waste. Waste is something that is not adding value to the final product. The 8 types of wastes are- Overproduction, waiting, transportation, inventory, motion, over-processing, defect, skill.
1.Overproduction: Due to producing more product than required.
2. Waiting: Time wasted waiting for information, material, and structure.
3. Transportation: Excess movement of people, tools, inventory, equipment, and other things of a process.
4. Inventory: Occurs due to storing more product and materials than required. Can cause damage and defect to materials, and waste of capital due to the extended time in store.
5. Motion: Time and effort wasted due to unnecessary movement of people, equipment, and machinery.
6. Over-processing: More work, more component, more steps in the product or service than required.
7. Defects: Products that fail to meet customer expectations.
8. Skill: The waste of human potential, and under-utilizing talent of the employees, and proving tasks without proper training.
There are different tools used in lean that can effectively optimize waste production and together they can be used to maximize the result. But this is just one aspect of lean six sigma.
On the other hand, in six sigma there are multiple tools and techniques for process improvement and removing defects.
There are 2 major methodologies of six sigma.
- DMAIC (for existing product improvement)
- DMADV (for new products)
Let’s discuss DMAIC:
- Define: Goals of the project are determined.
- Measure: Measure the performance of the current unaltered process.
- Analyze: Find out why the defect exists.
- Improve: Performance can be eliminated by addressing and eliminating the root causes.
- Control: Make regular adjustments to control the process and future adjustments. Continuous monitoring can give the authority an even better idea.
This will lean to decreased process time, increased performance, and customer retention.
In the lean six sigma implementation process, both lean and six sigma tools are simultaneously applied. As a result, the performance of the company improves rapidly as the waste level is decreasing and the performance is increasing continuously.
Lean six sigma tools:
1. JIT (Just in Time): Reduce the time that the production process takes and thus minimizes the response time.
2. 5s: Focuses on the cleanliness of the organization increasing efficiency and profits.
3. Kanban: Visual method to manage tasks and workflow. Visual workflow helps to identify issues in the workplace and it becomes easier to fix them.
4. Value stream mapping: This tool helps to identify:
- Value enabling activities
- Value-adding activities
- Non-value adding activities
5. Regression analysis: It is a statistical tool that helps us to estimate and understand the relation between two different variables. One of them will be dependent and another will be independent.
6. Pareto chart: A powerful tool that helps to find out the major causes of all the problems that are occurring in the industry.
7. Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Kaizen is the process of continually observing, identifying, and implementing incremental improvements in the manufacturing process which encourages all managers and employees to be involved in the process of manufacturing improvement.
8. Poka-yoke (Mistake Proofing): Poka-yoke is a Japanese term that means mistake-proofing. It is a process by which employees work to identify and eliminate the causes of human errors throughout the manufacture and production processes.
Also read: What is Six Sigma | What is lean six sigma | Six sigma application in textile industry
Principles of lean six sigma:
- Always focus on the customer:
Customers are the heart of any company. No company can be profitable without the support of its loyal customers. Lean six sigma works based on pull strategy, not push strategy, which means the produced products and the quantity of those products are dependent on the customer. That’s why customers should be the primary focus.
- Identify how the work is being done:
It is really important to understand the value stream of the process to find out what are the activities that are adding value to the product and what are the avoidable activities.
- Ensure a smooth process flow:
To get maximum output from the production line efficiency must be maximized. For this the process must be smooth, the authority has to make sure that there is no bottleneck in the line and the work distribution is done properly.
- Remove non-value-adding activities:
These are those activities that are not adding any extra value to the final product. Customer does not care about these activities and they are not going to pay for these. So, these activities must be removed from the process.
- Manage by facts:
Do not depend on assumptions, check the facts regularly find out the process improvement. Always try to reduce waste as much as possible.
- Involve people in the process:
Employees are the heart of an organization, make them a part of the system, part of the family. In this way, they will be more encouraged to work for the organization up to their full potential.
- Systematic improvement:
Haphazard, unplanned improvement activities will not bring any positive results. At first, do proper planning, prepare a workforce to work on this plan, and then go for implementation. This will bring the best result for the organization.
Benefits of lean six sigma:
- Increase in profit
- Standardized and simplified process
- Reduced error
- Employee improvement
- Value to the customer






0 Comments