What is ‘Six sigma’?
- The concept of six sigma is a set of tools and techniques that are used to remove defects and minimize variability from the process. It used a bunch of quality management methods, mainly statistical methods. As a result, the process efficiency increases, and the output product become defect-free.
- This was introduced by Bill Smith in 1986 and initially used at Motorola. Later Jack Welch used this tool in his central business strategy at General Electronics in 1995.
- For proper implementation of ‘Six sigma’ a group of people is employed or hired in the company who are experts in this aspect and they help the other employers of the company to properly implement the tools and techniques. Six sigma believes in high-level cross-functional processes where top management is also involved.
The focus of six sigma:
Six sigma always focus on those aspects that are highly important for the organization. It also focuses on the proper planning of the projects and quantifying the result.
Benefits of Six sigma?
If properly implemented, six sigma can be highly beneficial for the company. The company will have:
- Reduced process cycle time.
- Reduce pollution.
- Reduce cost.
- Increase in efficiency.
- Increase customer satisfaction.
- Increase in profit.
Generally, all the critical projects are top-down, but six sigma allows the initiation of the projects at any level of the organization as long as the aim is realized.
What is lean six sigma?
Lean six sigma means a collaborative effort to improve the performance of the company by using two separate tools. One is lean and the other is six sigma. As we discussed earlier, the purpose of six sigma is to remove defects and reduce variability.
On the other hand, the purpose of lean is to reduce waste.
Type of waste:
There are seven types of waste.
1. Defect: Any kind of defect in the product leads to rework and causes a waste of time and resources.
2. Over-production: Over-production causes waste of time, resources, and manpower.
3. Waiting: It is a very common waste in the factory. Mainly is causes due to improper work distribution or defective machines. Waiting results in a waste of time and manpower.
4. Non utilized talent: It means not using the workforce up to its fullest potential. It causes a waste of manpower.
5. Transportation: Unnecessary movement of the products causes due to the lack of planning. It causes a waste of time and energy.
6. Inventory: Extra inventory due to improper planning causes a waste of money and resources.
7. Motion: Unnecessarily moving products and raw materials from table to table causes waste of manpower and time.
8. Extra processing: Extra processing causes waste of time, resources, and manpower. This is one of the most common wastes in the factories.
Is lean is also applied with six sigma then it will be highly beneficial for the company because on one hand six sigma will improve the process and on the other hand lean will ensure the waste is also decrease.
 |
| Types of waste |
Six sigma percentage values:
Six sigma values are derived by using a normal distribution. It is a bell-shaped curve ranging from -6σ to +6σ. Here σ means standard deviation. The value of the output is generally measured by mean or average. But the output quality of every measurement will vary from each other. As a result, the shape of the curve changes.
 |
| Normal distribution curve |
The following chart shows the sigma value, the accuracy level, and the defect level:

Example: If a process has achieved a 6σ accuracy level. This means here, 6 is the standard deviation, there will be 3.4 defective output per million and the accuracy percentage will be 99.99966%
Six Sigma tools used in textile/garment industry:
DMAIC model:
Used for existing product improvement.
What is DMAIC?
DMAIC stands for:
Define: At first the problem is clearly defined.
Measure: Data is collected at a regular interval.
Analyze: After the collection of data, they are properly analyzed to find out the cause of the problem.
Improve: Appropriate action is being taken by the management to improve the current situation.
Control: Future changes are tested and evaluated to maintain the standard.

Also read: 7 six sigma tools to improve the performance of a company | What is six sigma | What is lean
Also if both lean and six sigma are applied in the company then ‘JIT’ is also applied.
What is JIT?
- It is a manufacturing philosophy that is based on eliminating waste and continuous improvement of productivity.
- In this methodology, the supplies and products are pulled through the system to arrive where they are needed, when they are needed.
- The mandate of JIT is: “Eliminate all waste”.
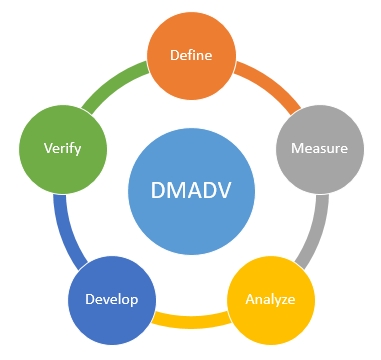
DMADV model:
What is DMADV?
Example of six sigma process application:
Ladies tank top production problem in a factory:
Scenario: Ladies tank top production is going on in the sewing floor. But after several inspection, it is identified that in a lot of the final garments the stitch around the neck and sleeve are wobbly and also the folds are uneven and in some cases open seam was found.
 |
| Problem areas in the tank top |
Application of DMAIC in this situation:
Define: Wobbly stitches, uneven folding, open seam around the neck and sleeves.
Measure: data is collected every two hours to find out the percentage of defective clothes.
Analyze: The data and the operation of the workers are analyzed to find out the problem.
Improve: It is identified that the problem is occurring due to the lack of control of the worker. A proper sized folder (1 cm in this case) is suggested to be used so that the worker can have a better control and fabric cannot move during sewing.
Control: Future data are also collected to maintain the standard.
 |
Folder is chosen from the folder library depending on the width of the fold.Six sigma application in textile and apparel industry:
Conclusion:Now a days 'Six Sigma' is very commonly applied in the textile industry due to its positive impact on the performance of the company. But to get the best result, all the employees need to understand what six sigma is and also direct involvement of the top level management is needed. |




0 Comments