What is ‘Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA)’?
- For a proactive quality control approach, it is necessary to know what potentially may go wrong with the process of producing the product or service or what may go wrong during the shipment or storing. There is a systematic quality tool that is built for such analysis, known as ‘Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA)’.
- FMEA is a proactive tool that aims to identify and prevent the process or product error before they even occur. For example: in healthcare, it is always said that “Prevention is better than cure”. If through regular we can find out what are the potential risk factors for us, then through proper care we can avoid any adverse effect. FMEA works in a very similar manner.
- FMEA was developed by the US military in 1949 but its practical application started almost a decade later.
Purpose of Failure mode and effect analysis?
If properly applied, FMEA will lead to a number of reductions. Such as:
- Failure during prototyping.
- Defects in production.
- Reworks in process.
- Failure during customer use will eventually lead to customer complaints and dissatisfaction.
- Warranty claims that will cause a waste of money and resources.
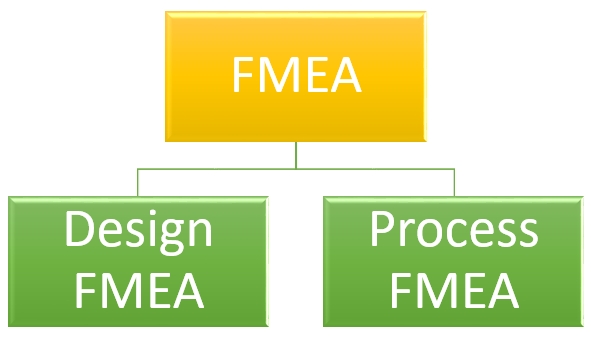
Types of Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA):
There are two aspects of a product, design, and process. So, FMEA deals with these two categories.
1. Design FMEA (d-fmea):
The assessment of critical points of the product is done, and the aspect that can potentially go wrong during manufacturing or during the period of use by the customer is identified. In this way,the weakness of the product is identified and addressed. Also, FMEA identifies the critical characteristics of the product which significantly affects the performance.
2. Process FMEA (p-fmea):
It analysis the process of producing the product or service. The process must be able to produce a product that meets all the design and performance requirements. The management and transactional process are also involved in it as they are also a part of continuous development.
Benefits of FMEA:
- Captures the collective knowledge of the team.
- Improves the reliability, quality, and safety of the process and the product.
- Logical, structural methods to identify the areas of concern.
- Reduces development time and cost.
- Documents and tracks risk reduction activities.
- Helps to identify the critical qualities of the product.
- Provides historical record.
- Provides baseline.
- Helps to ensure customer satisfaction and safety.
Also read: Pareto Chart with example | 3 real-life Pareto chart examples with explanation | Pareto chart application in textile
The procedure of FMEA:
- The intended function of the product or service is identified. The product or service must meet the requirements.
- Potential failure and their nature are identified, their impact, magnitude, and other consequences are also identified.
- A list of the causes of failure is prepared and their effect is also analyzed.
- Severity and likelihood of occurrence are determined and then rank is prepared.
- The rank is prepared in a descending order depending on the severity of cause and effect. For this purpose, “Risk priority number (RPN)” can be used.
Risk priority number (RPN) = P*S*D
Here,
P = Probability of occurrence
S = Severity of that incident
D = Detection; likelihood that the defect will reach to the customer.
- Method for the identification of all those failure modes are identified and then reviewed for effectiveness and accuracy.
- What will be the corrective action to help eliminate all the potential concerns, are determined.
- All the recommendations, corrective actions, and counteractions are constantly monitored to check for effectiveness.
- The entire cycle has to be repeated in case of any product development.
Example of “Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA): From theory to execution:
Let us consider an example of FMEA applied in the sewing line of a textile factory:
On that line ladies, band collar polo is produced and it is considered to be a critical item. A lot of the output products may fail to meet the quality requirement. That’s why it is necessary to take proactive measures.
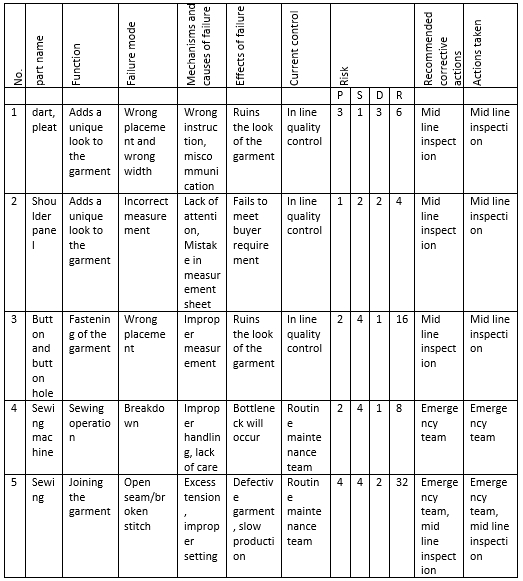
At first design FMEA is analyzed, the garment has a lot of cut panels and after analyzing all of them some potential issues are identified:
- Wrong dart, pleat measurement.
- Incorrect measurement of shoulder panel.
- Improper placement of button and buttonhole.
- Machine breakdown.
- Open seam/broken stitch.
- Uneven button stand width.
- Fold in the collar.
- Yellowish collar.
All these potential issues are thoroughly analyzed and then the FMEA form is prepared.
Failure mode and effect analysis (FMEA) template:
An example of the FMEA form is shown below depending on some issues mentioned above:
P= Probability of occurrence
S= Severity of occurrence
D= likelihood that the defect will reach to the customer
Here,
1- Very low/none
2- Low/minor
3- Moderate/significant
4- High
5- Very high
Conclusion:
When properly applied, FMEA prevents potential failure and thus it saves a lot of time, money, and resources of the company. It ensures that the product, process, and service are defect-free and reliable. FMEA should be considered as a tool for continuous improvement, and not just a catalog of potential failure. It must not be considered as a paperwork exercise because it will limit its usefulness.




0 Comments